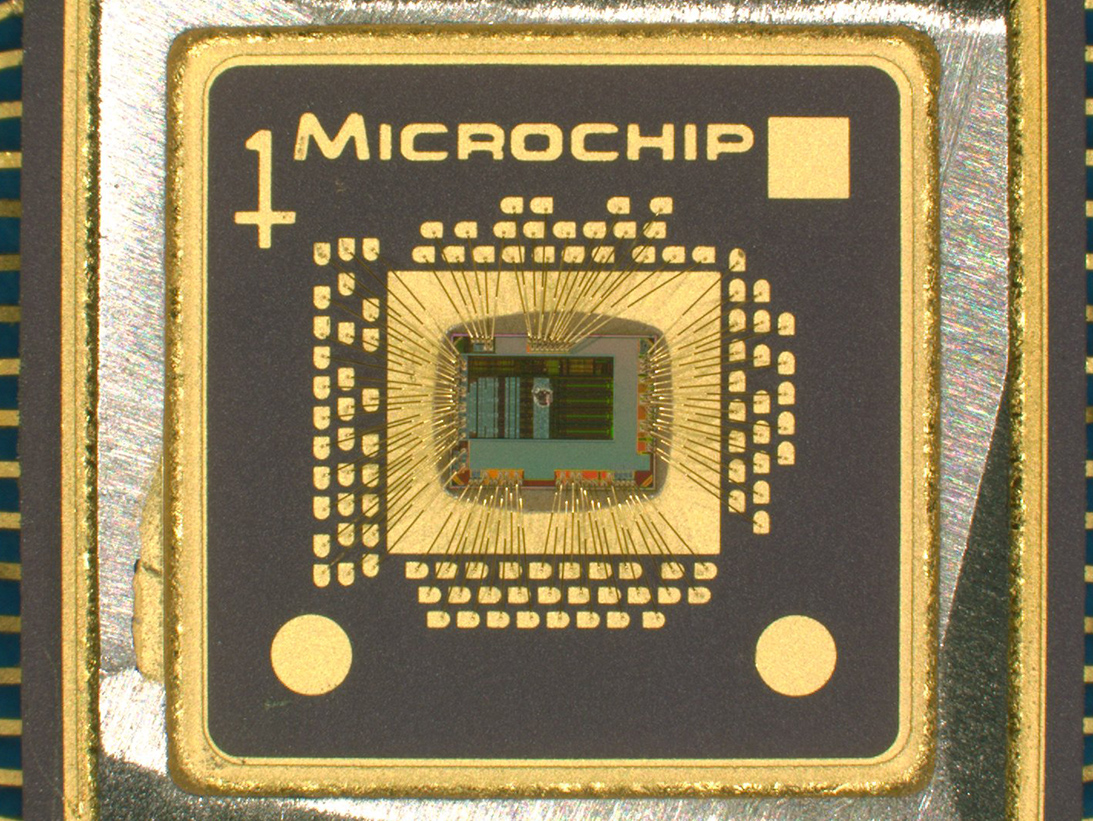
Destructive Physical Analysis (DPA) Testing for Microcircuits
Microcircuits are common components and essential to the function of nearly all electronic systems. Due to their wide-ranging applications, packaging of discrete Microcircuits will vary to meet environmental, power and application requirements.
Typical Microcircuit package designs include Hermetic – ceramic and metal housings with lid-seam weld or solder seals, glass-frit seals, and a multitude of non-hermetic plastic encapsulated (PEM). All are prevalent in Aerospace, Military and Automotive systems. Within the scope of Aerospace applications, Microcircuit devices are subjected to qualification requirements of MIL-PRF-38535 and/or Methods for DPA to MIL-STD-1580 and MIL-STD-883.
Dual Cavity Hermetic
Ceramic
Ceramic Flat Pack
Hermetic Flat Pack
Surface Mount Device
Plastic TSOP BGA
ORS offers FAST Reliable Microcircuit DPA
Microcircuit device construction variations require specific test methods in DPA testing based on military performance specifications (Mil-PRF) and design drawings.
Microcircuits for Aerospace applications must meet DPA MIL-STD-1580 Requirement 16 that specifies testing to Methods of MIL-STD-883 and requirement 9 prohibited materials analysis. Specific test methods will vary based on applicability to the design or construction. Terrestrial systems depending on class may specify DPA procedures listed in Mil-Std-883 Method 5009. All designs require external visual inspection, X-ray radiography, some form of internal visual inspection and prohibitive materials analysis (PMA) for elemental constituents of packaging materials.
Additionally, testing of hermetic packages includes testing to Methods 1014, Hermeticity and method 1013 Internal gas analysis, as well as wire-bond strength and die-shear testing methods 2011 and 2019. Glassivation layer integrity Method 2021 and possibly SEM metal inspection to Method 2018 may be required.
Plastic encapsulated devices typically require acoustic microscopy, cross-sectional inspection with dye impregnation, bond pull (if applicable) and SEM metal test methods, depending upon metallization patterns, as specified in Requirement 16.5 of Mil-Std-1580.
Destructive Physical Analysis
ORS has over 40 years of experience performing comprehensive testing designed to identify anomalies that can lead to field failure.
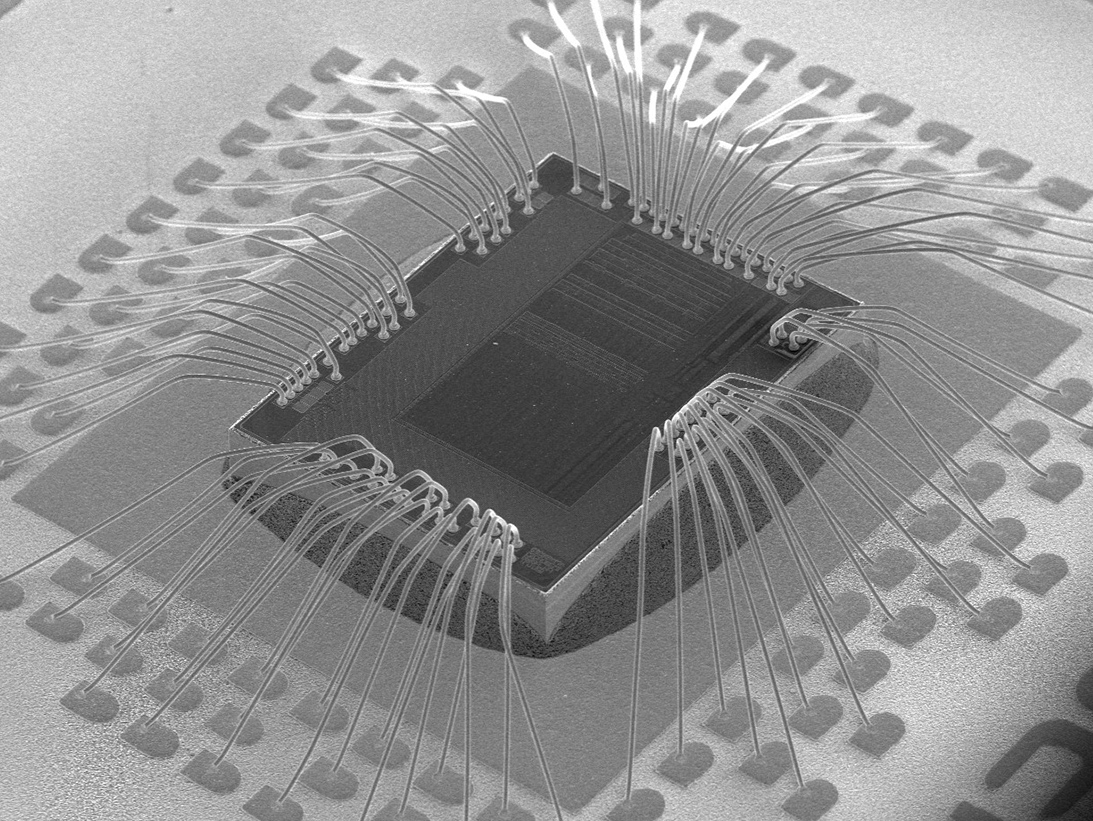
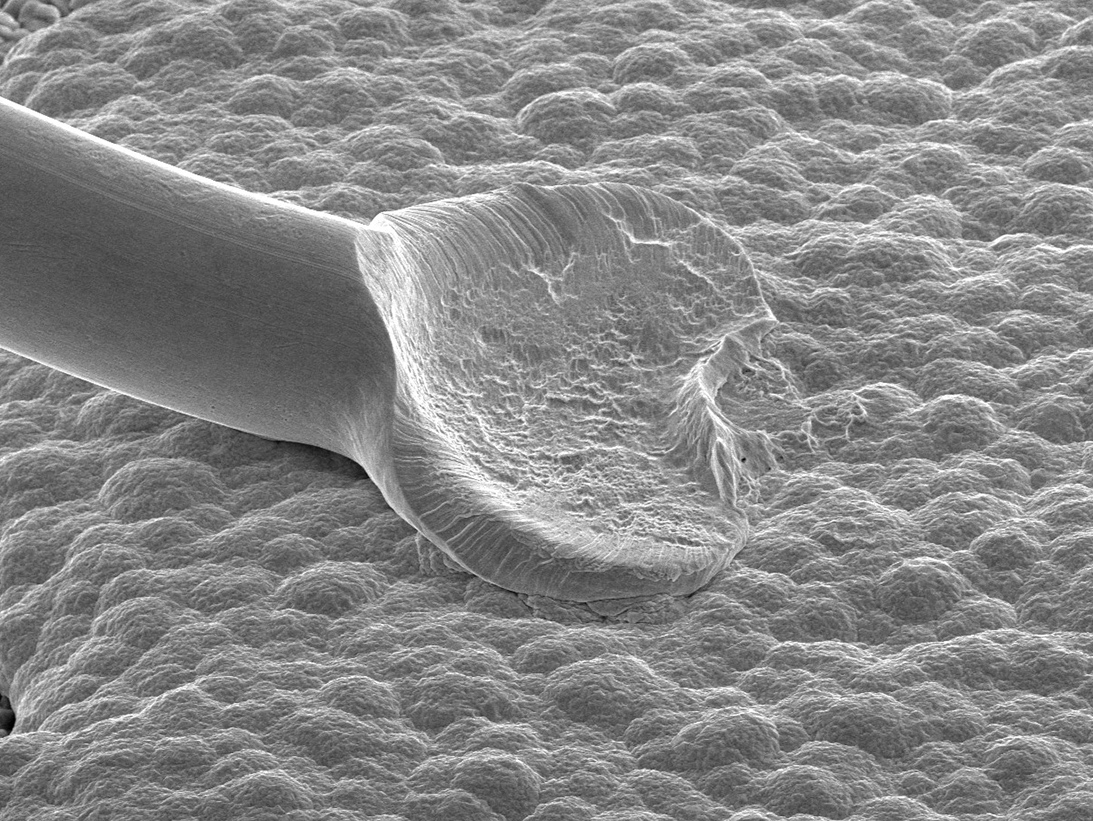
ORS DPA techniques for Microcircuits have effectively revealed imperfections that include improper package markings, hermetic seal failures related to lid-seal and glass feed-through anomalies, bond wire placement, bi-metallic bonding, intermetallic formations and wire-to-lid clearance, die attachment voiding and adhesion, and die-metal voiding and contact-step thinning.
ORS has been granted suitability for most DPA methods per MIL-STD-883, MIL-STD-750 and MIL-STD-202 by Defense Logistics Agency (DLA).
Contact us for information about microcircuits testing
Non-Destructive Test Methods
An important part of a Microcircuit DPA are the applicable initial non-destructive testing methods – external visual inspection with physical dimensions/configuration compliance, X-ray Radiography, acoustic microscopy, Hermeticity, particle-induced noise detection (PIND), and prohibited material analysis (PMA) by X-ray fluorescence elemental analysis (XRF) along with Fourier transform infrared microscopy (FTIR).* These methods can be essential to determining subsequent destructive test methods.
*FTIR is commonly included in baseline DPA or Construction Analysis (CA) tests to document functional groups detected in mold compounds and other organic features (i.e., die conformal coating and Leadframe adhesives).
Ext Visual Lid Seal
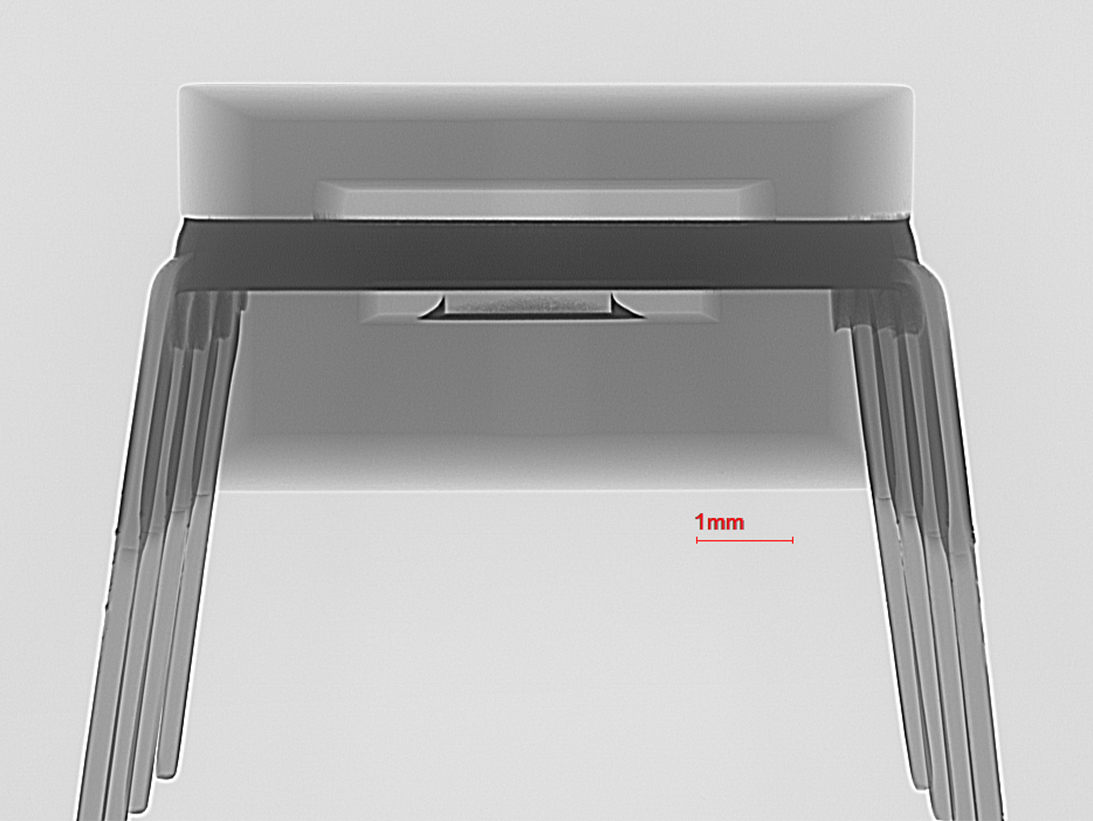
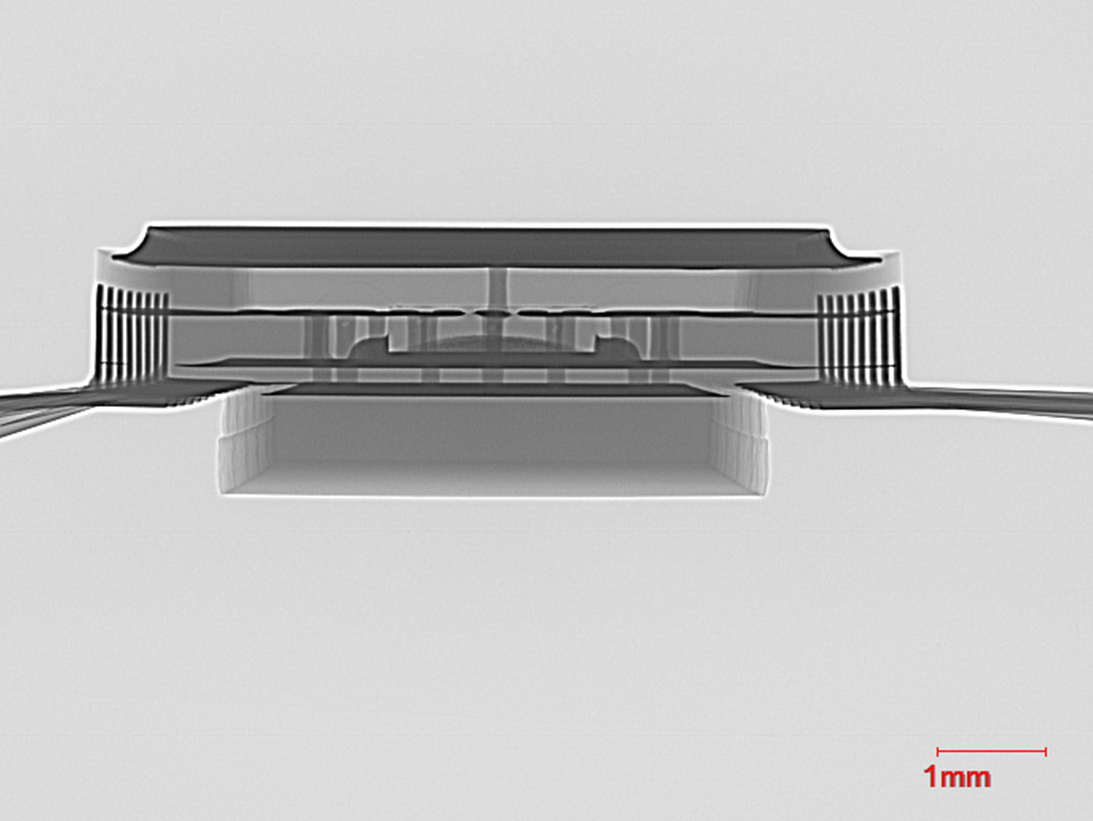
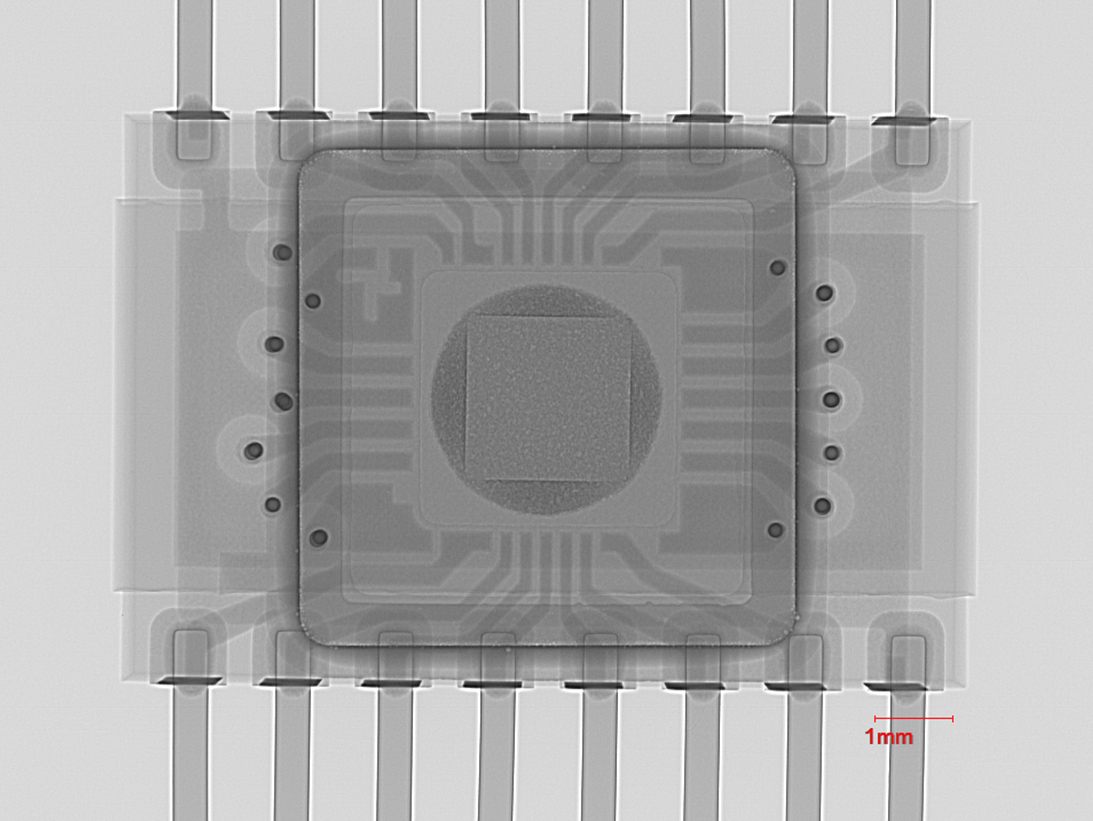
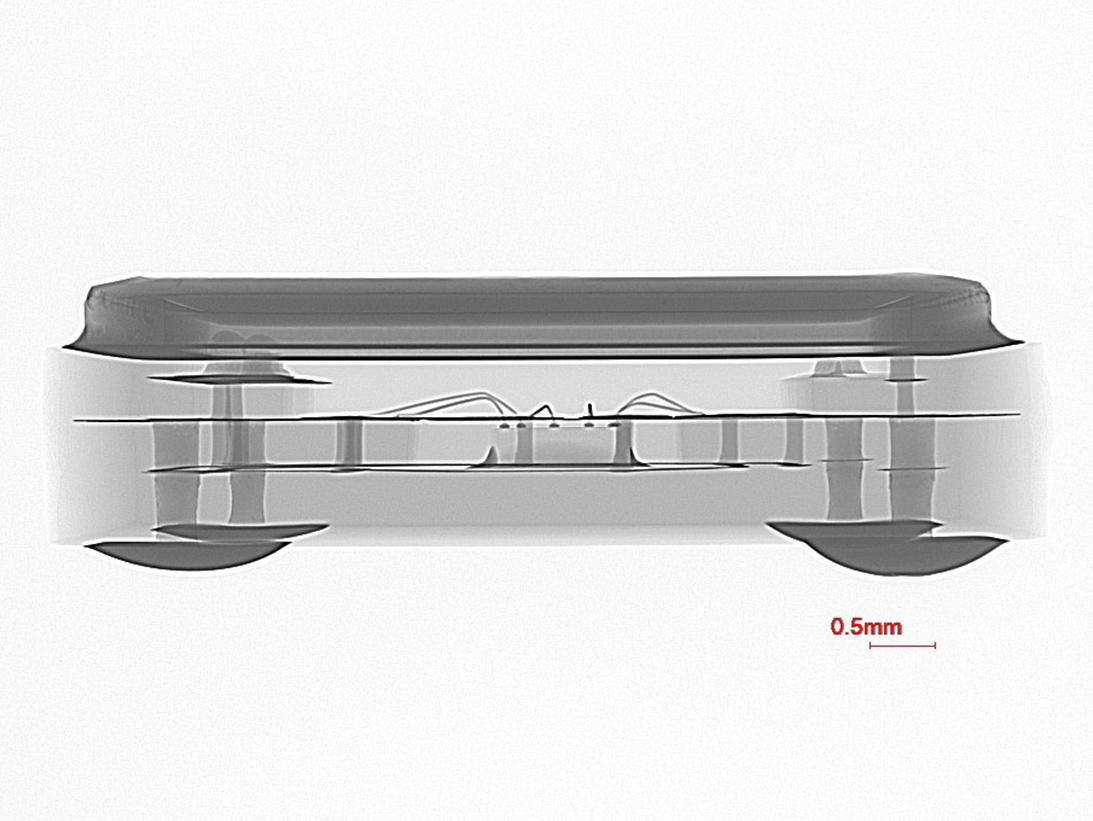
Z-Axis X-Ray View
Y-Axis X-Ray View
Ceramic Glass Frit Seal
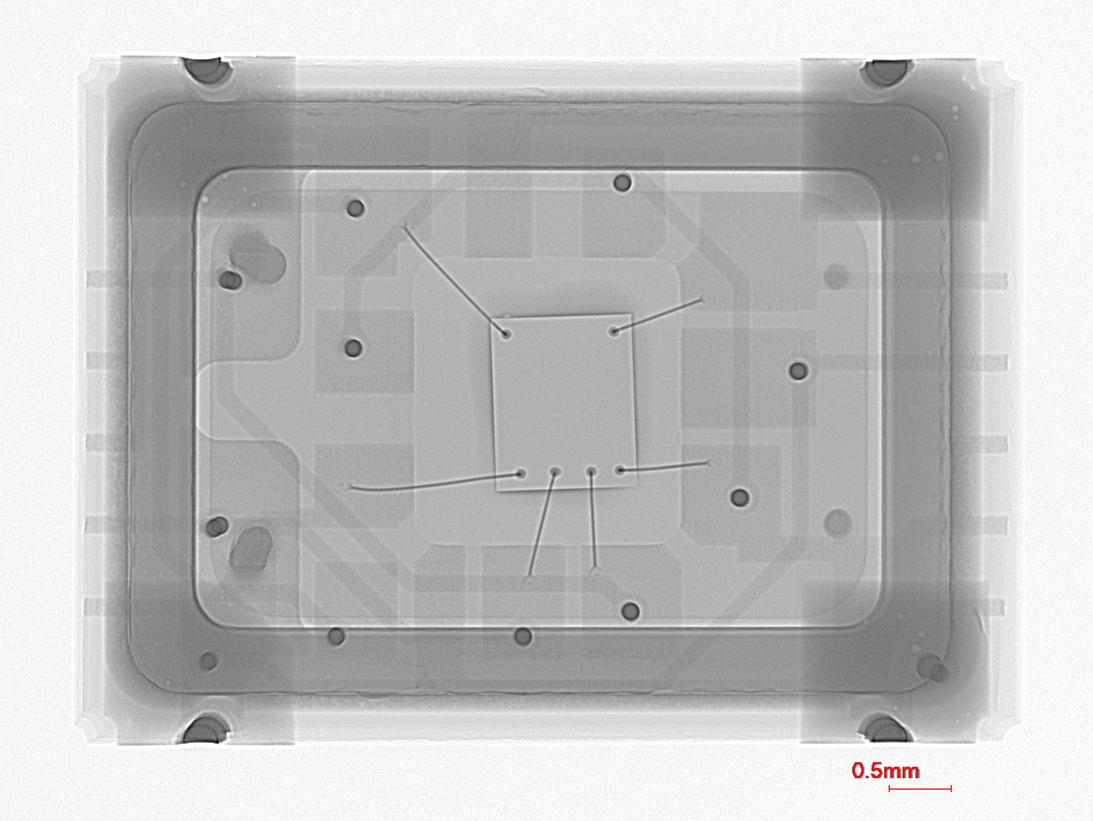
Z-Axis X-Ray View
Y-Axis X-Ray View
SEAM Weld SMD
Y-Axis X-Ray of SMD
Y-Axis X-Ray View
EMC
Y-Axis X-Ray Image
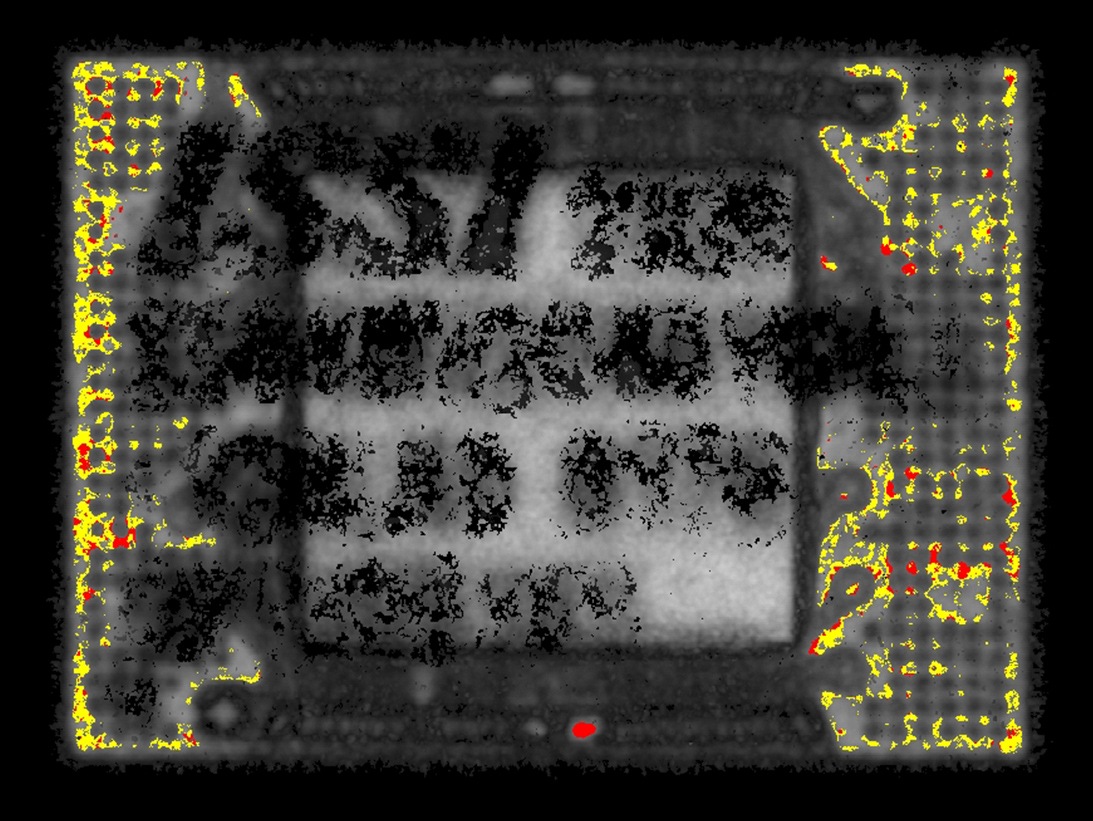
Acoustic Image
Destructive analysis methods of Microcircuit testing
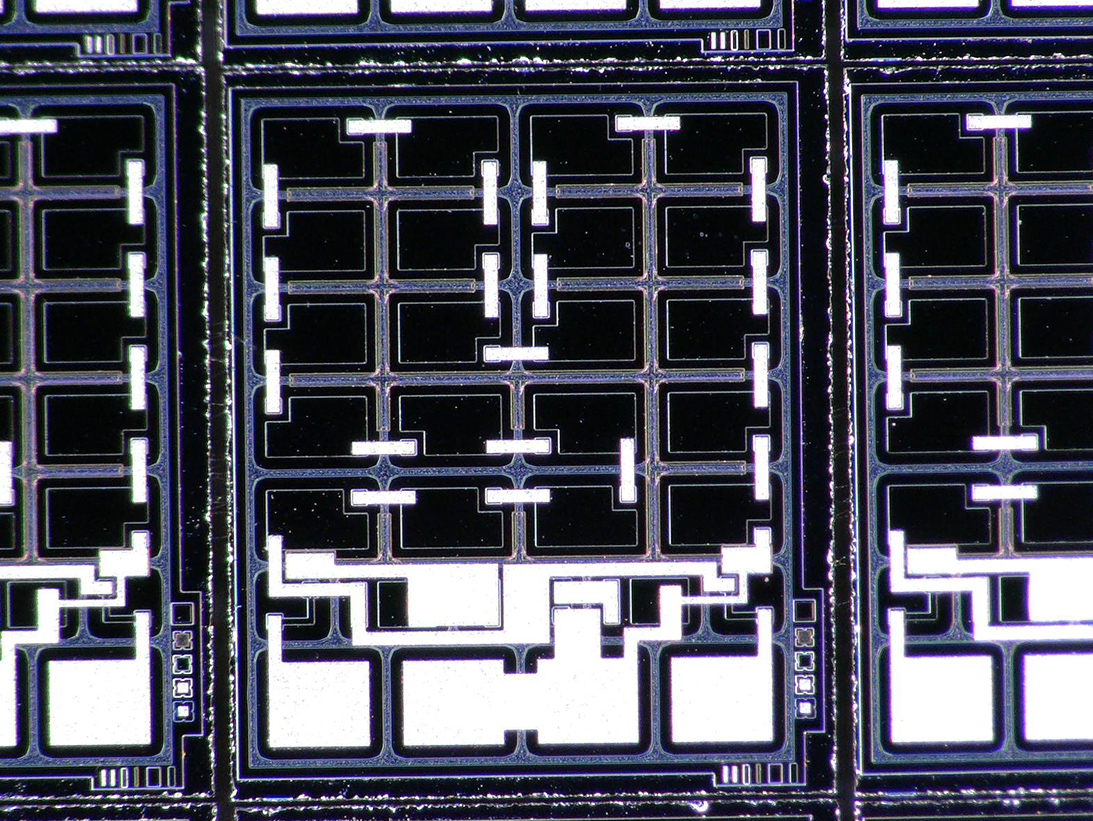
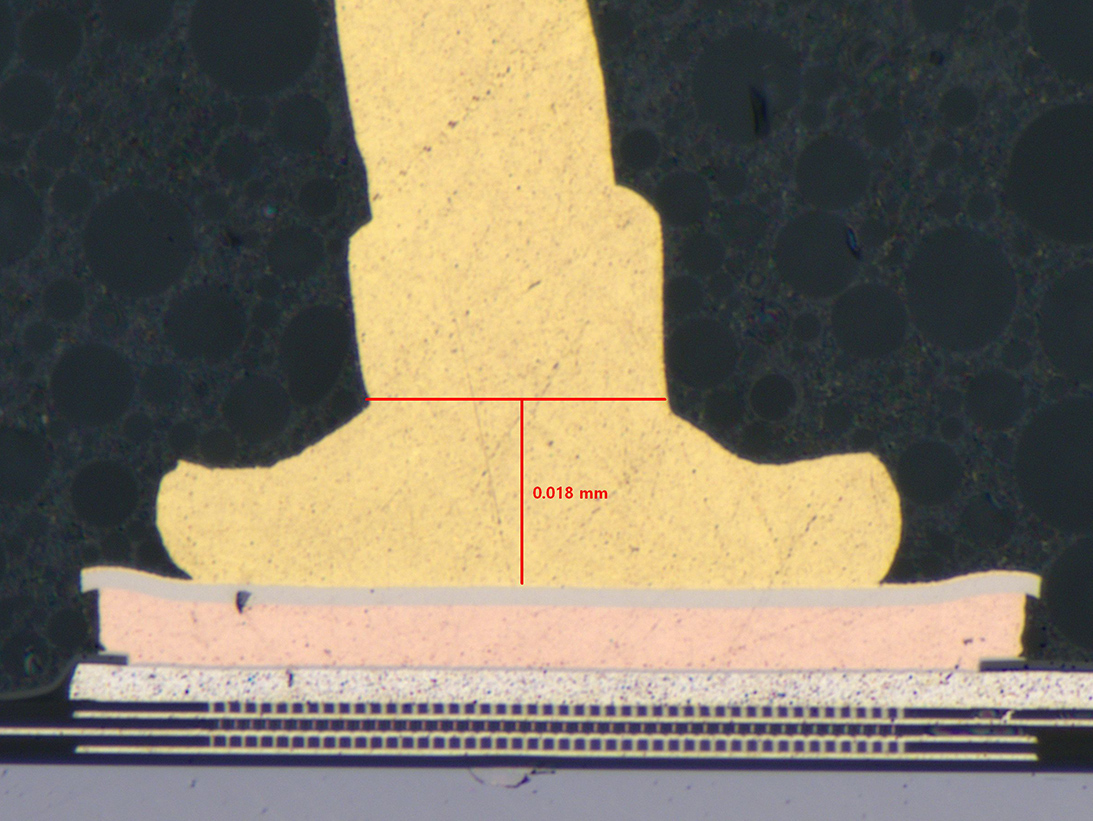
A complete DPA of Microcircuit could include destructive test methods such as internal gas analysis (IGA), internal visual inspection achieved by de-lidding/de-encapsulation or by cross-sectioning, bond strength testing, scribe and break methods. Microcircuit die with expanded metal require scanning electron metal inspection (SEM). SEM with energy dispersive X-ray (EDS) analysis may be utilized for internal prohibitive materials analysis testing.
Internal View of Ceramic
SEM Image of Cavity View
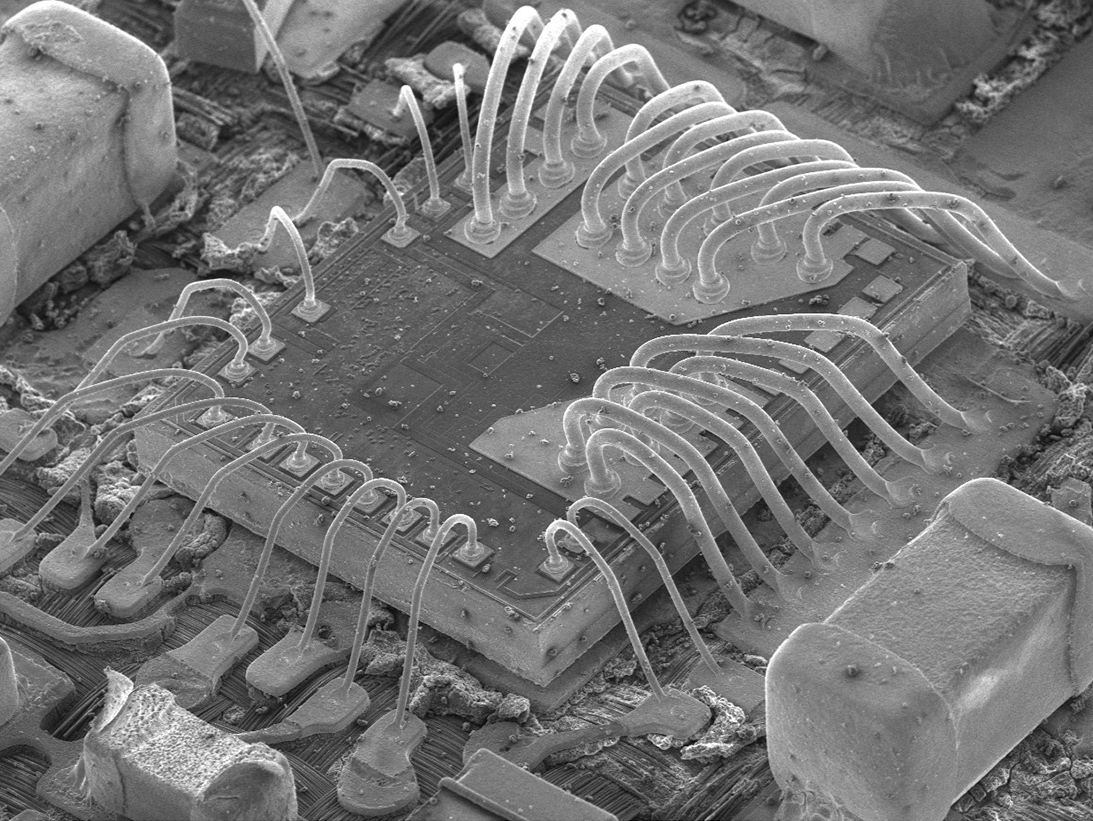
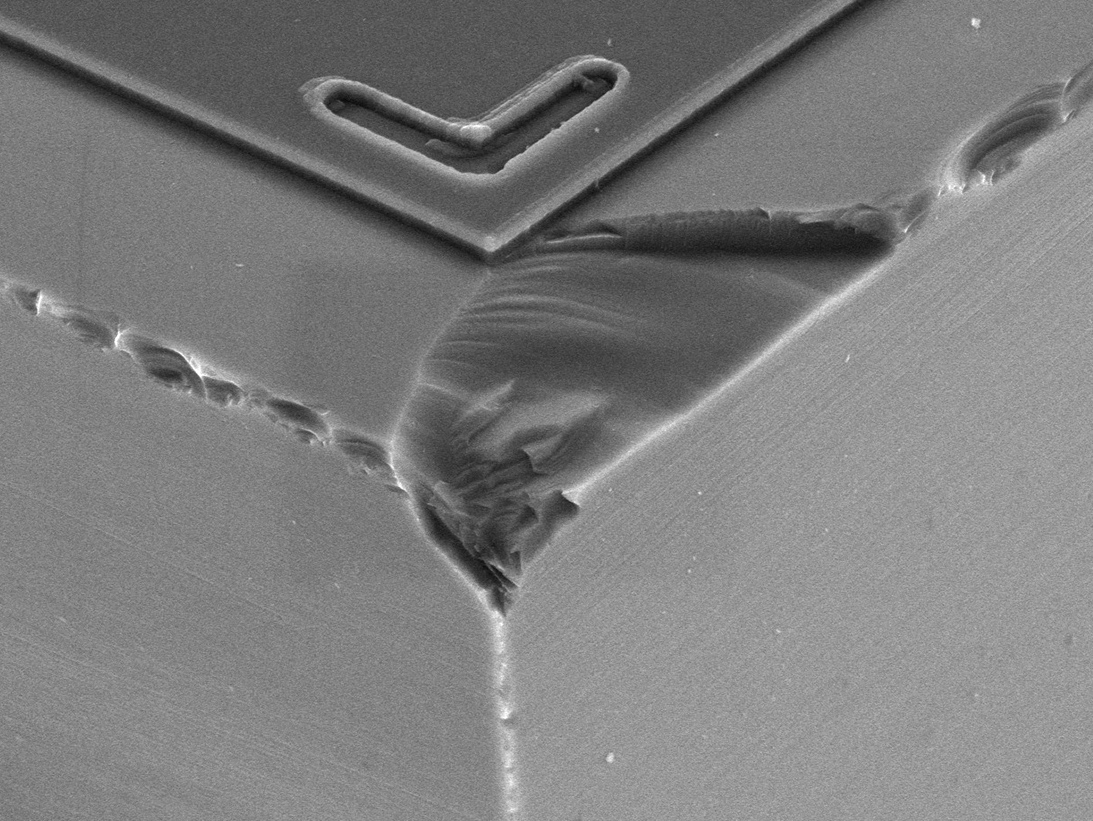
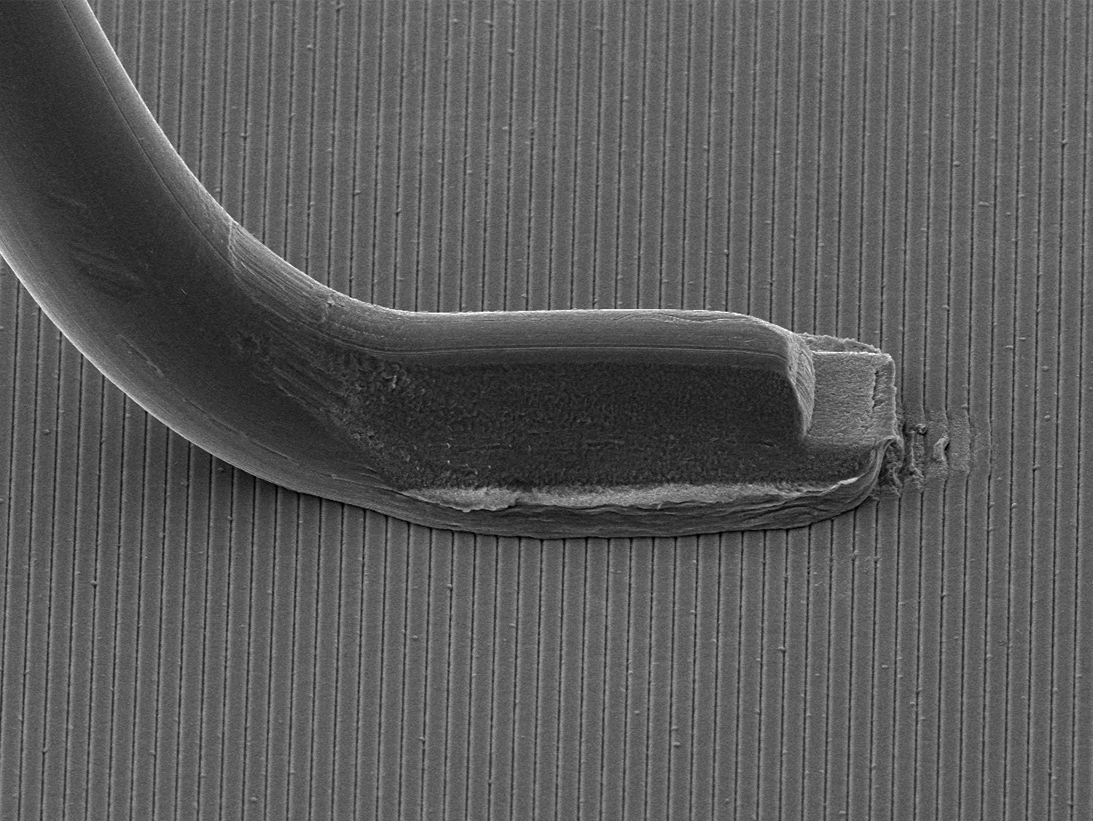
SEM Image of Bond
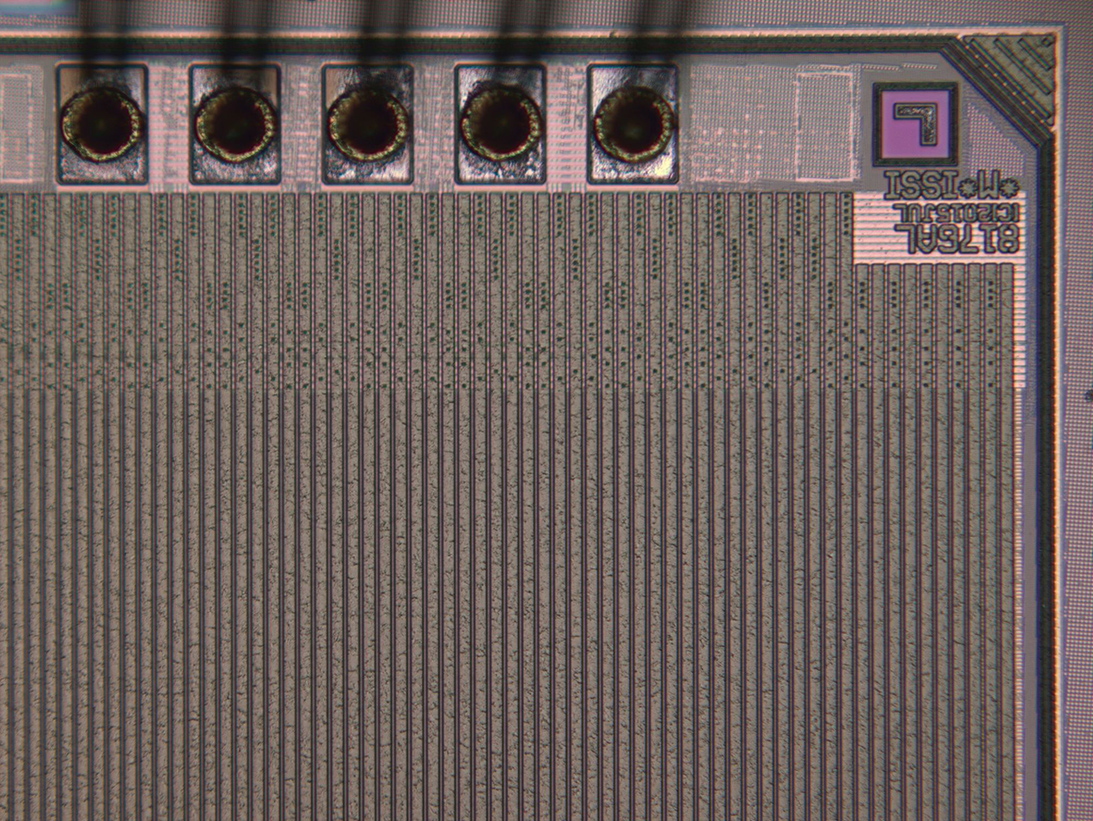
Wafer Dice
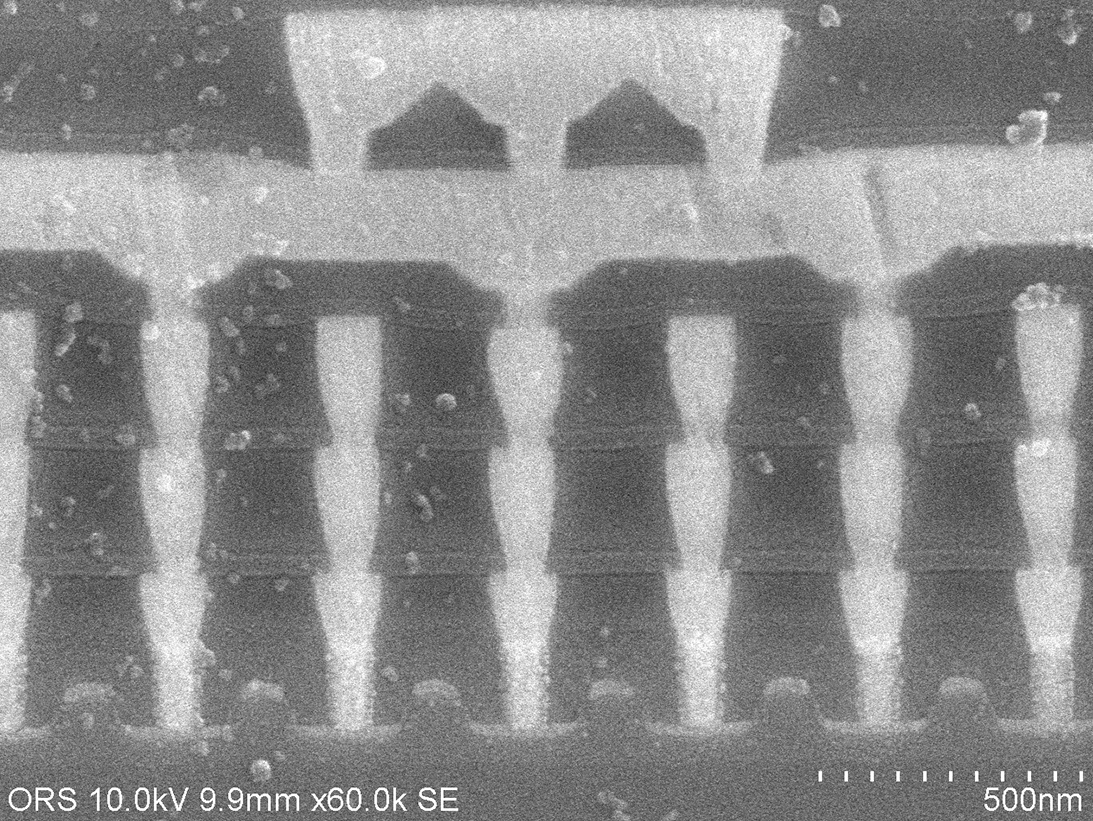
SEM Image of Metal
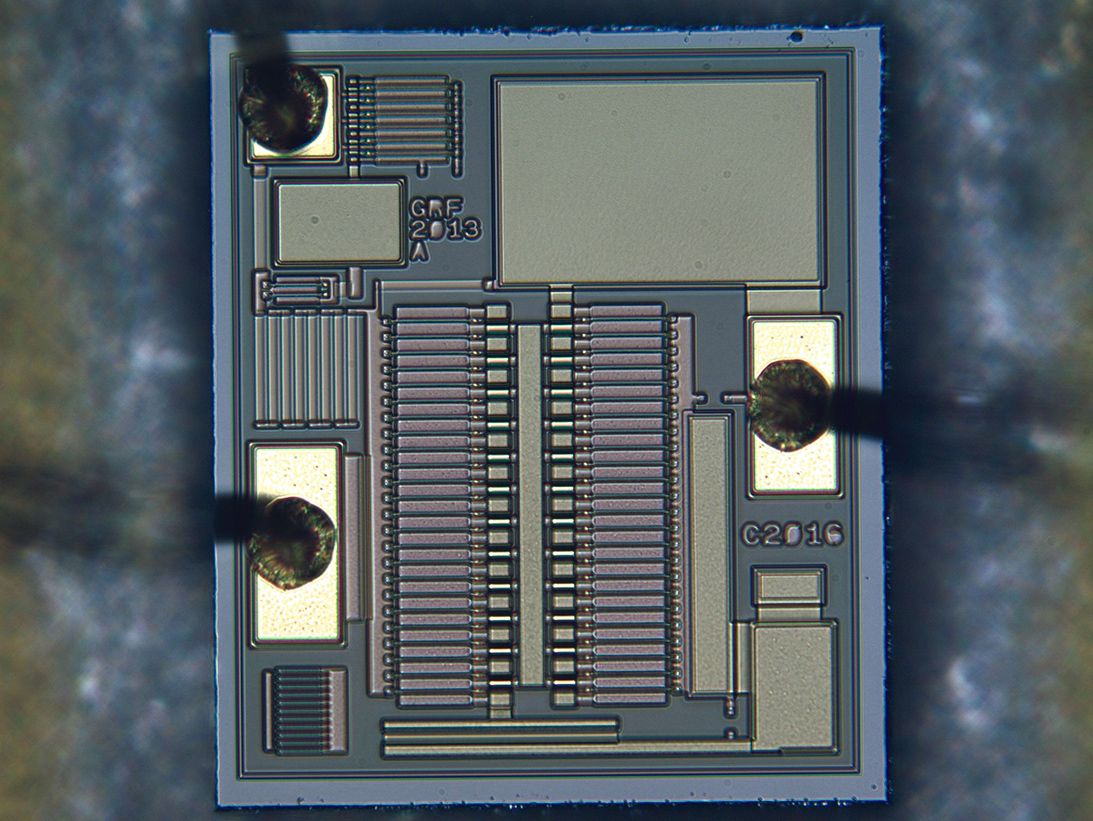
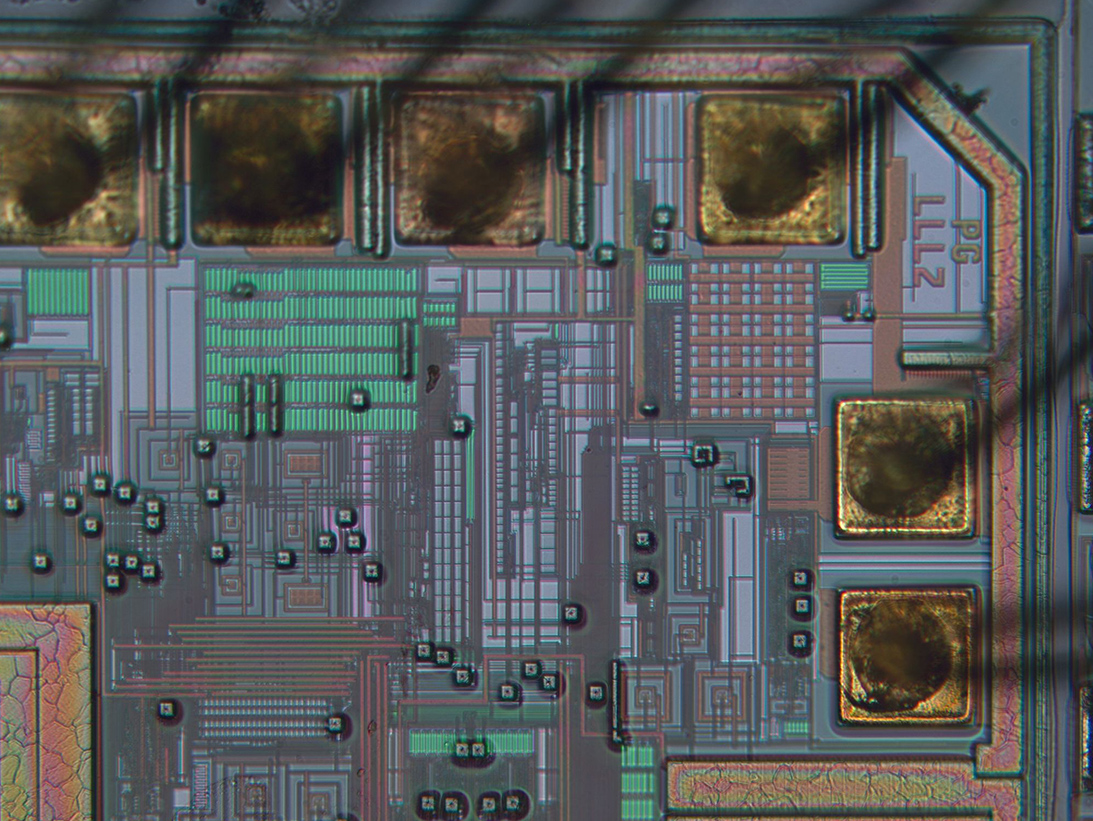
SEM Image of Planar Die
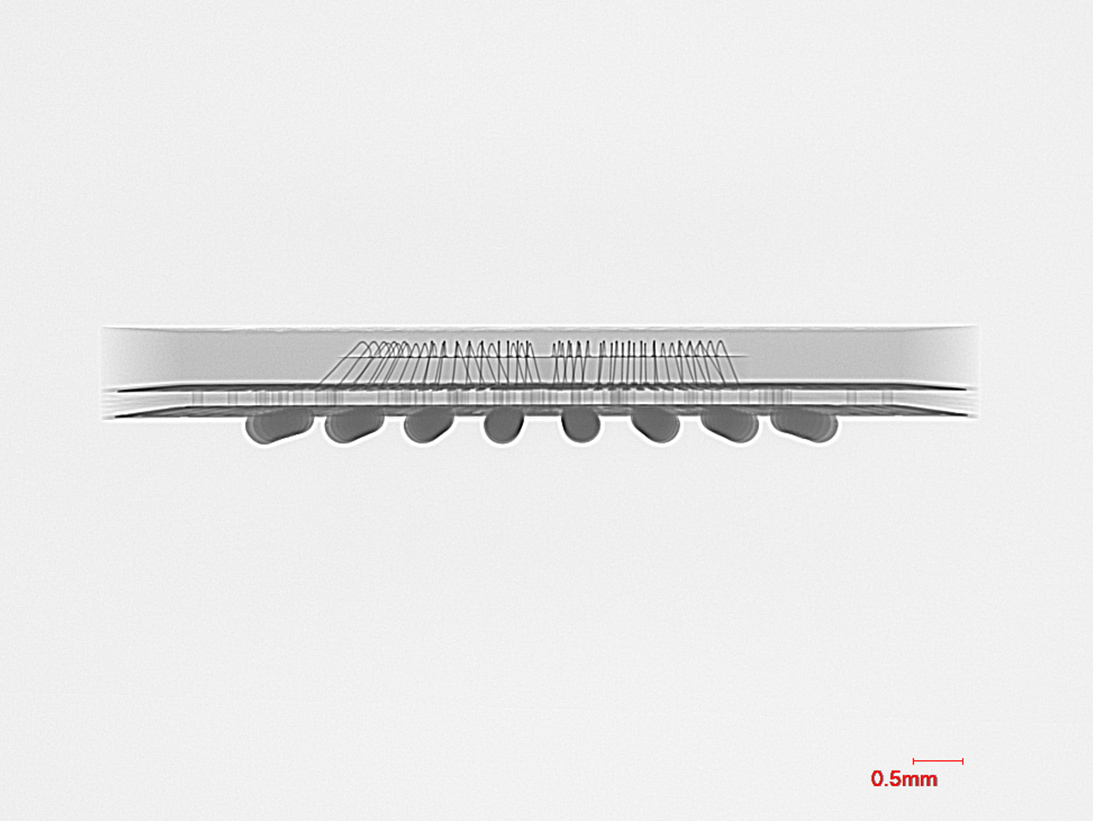
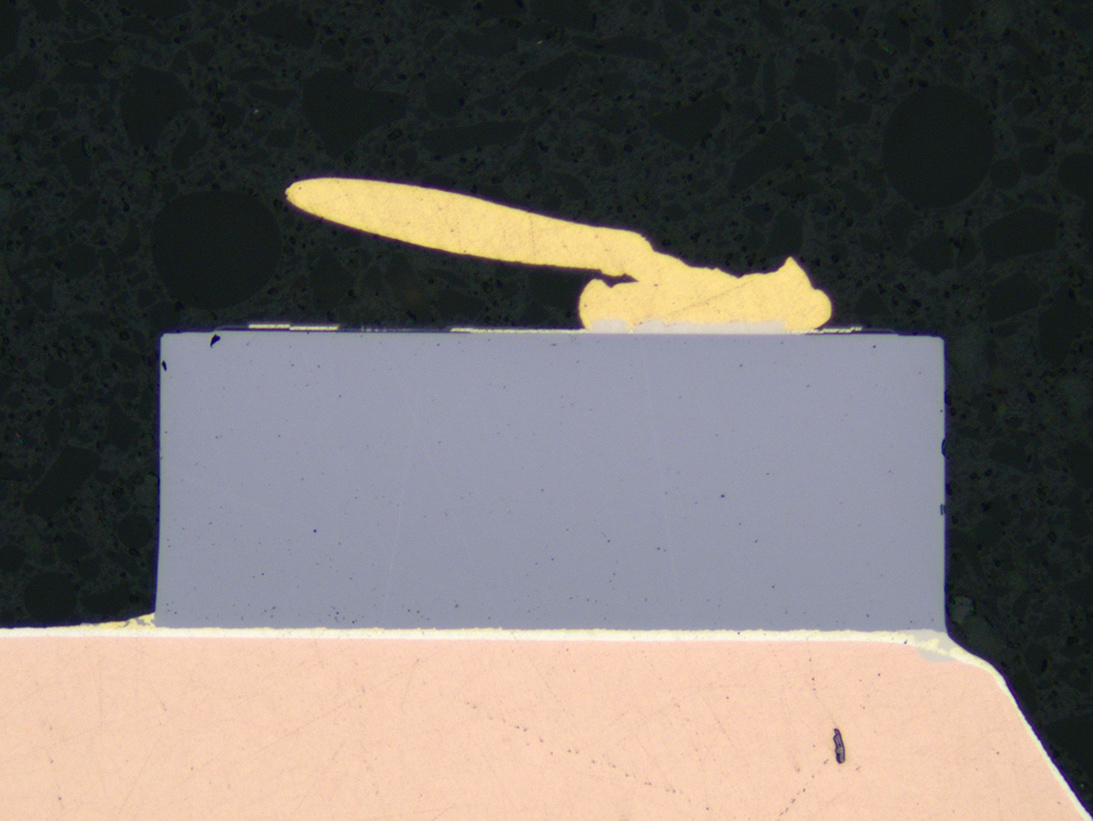
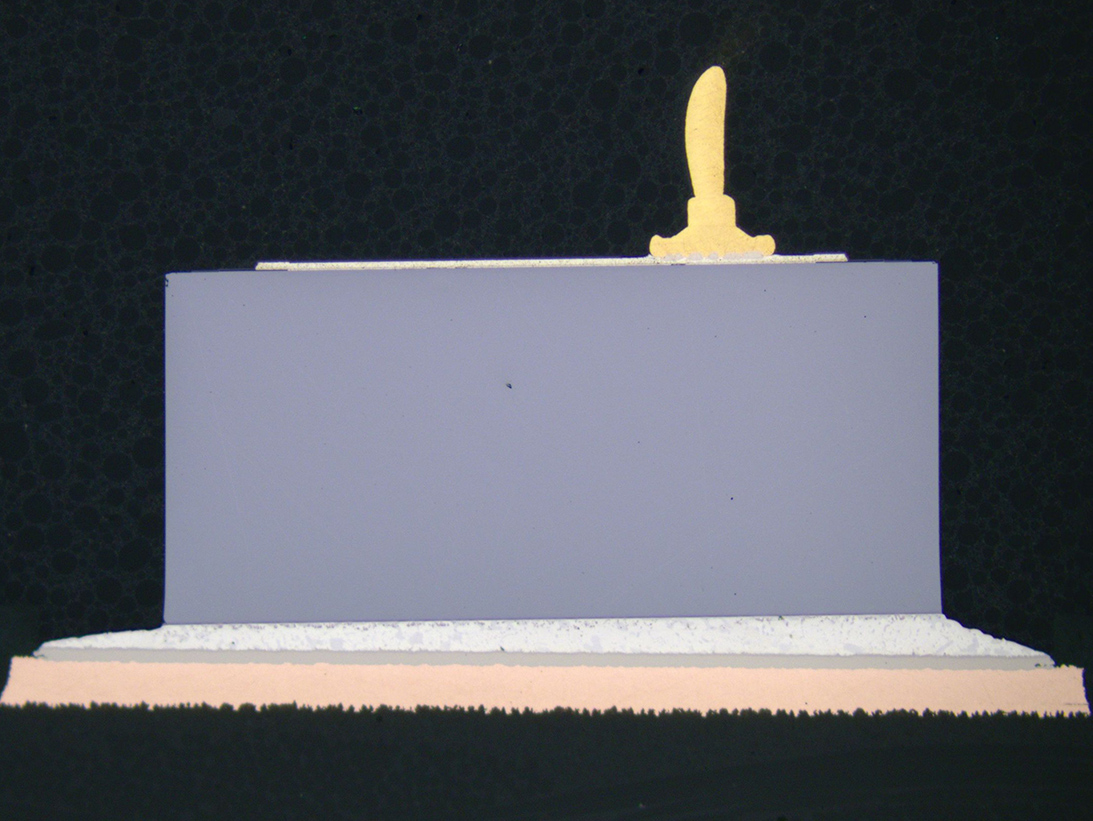
X-Sec View of BGA
Secondary Bond
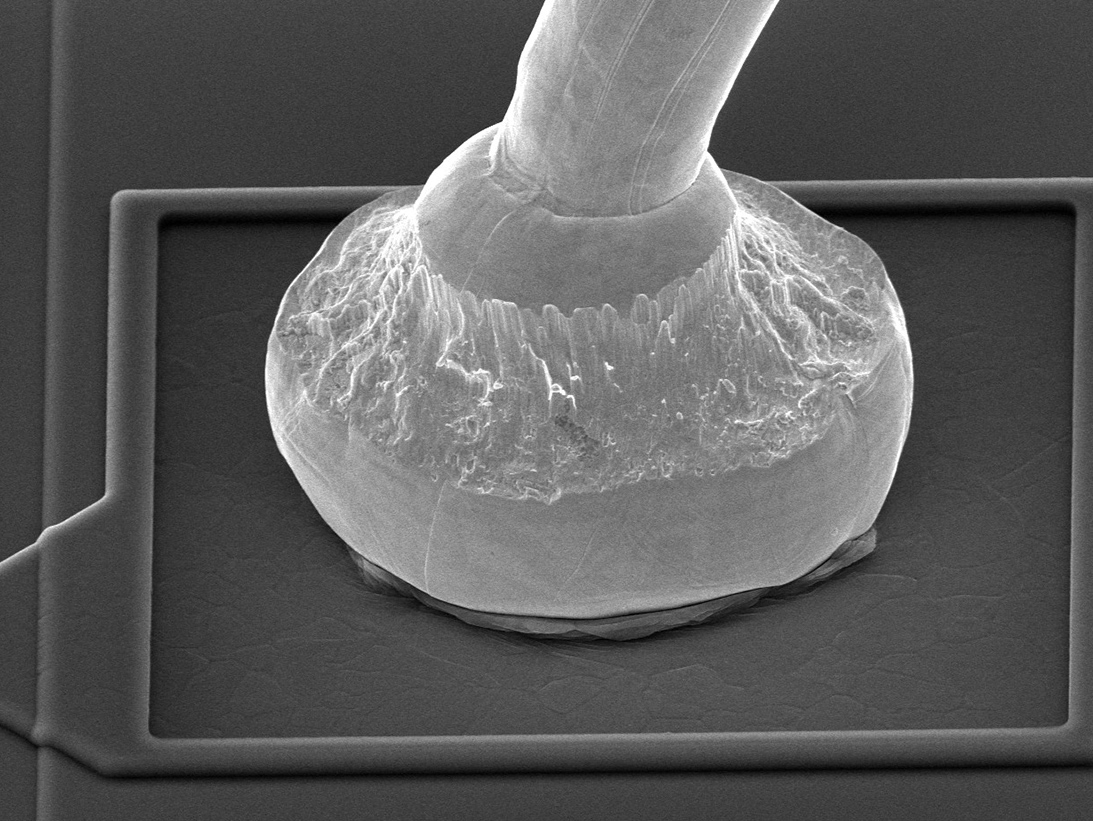
Solder Ball
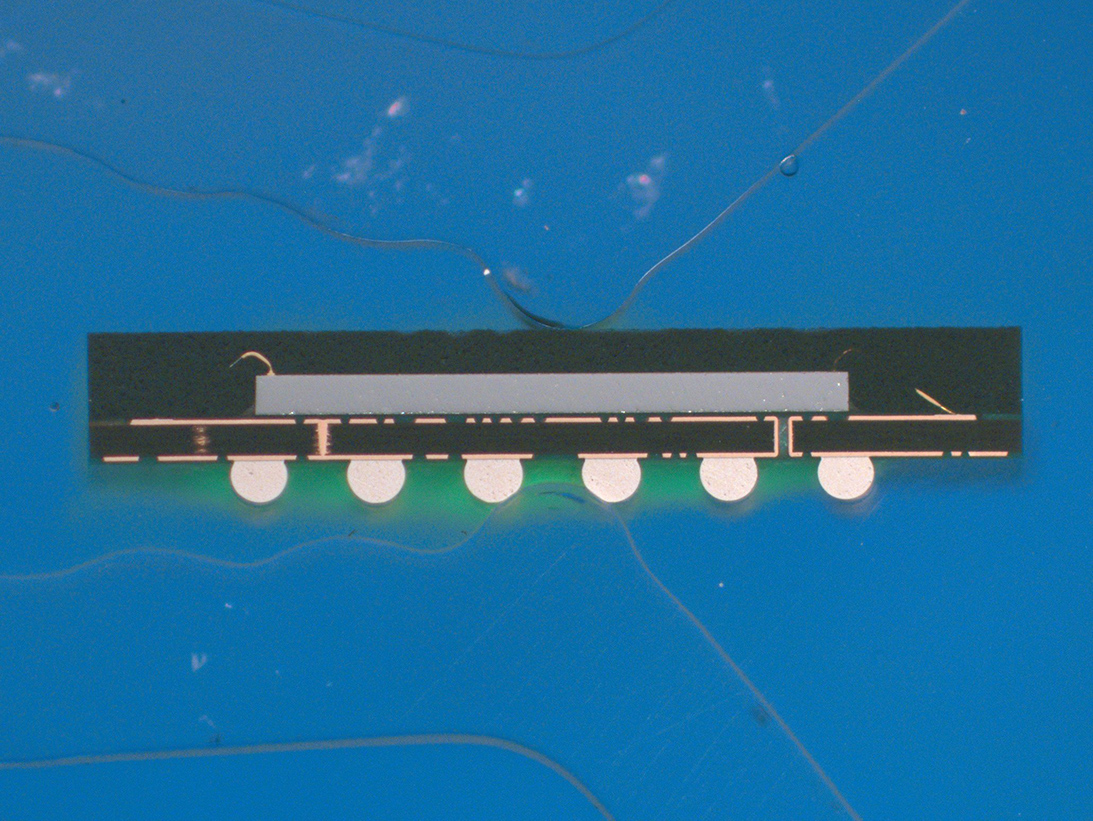
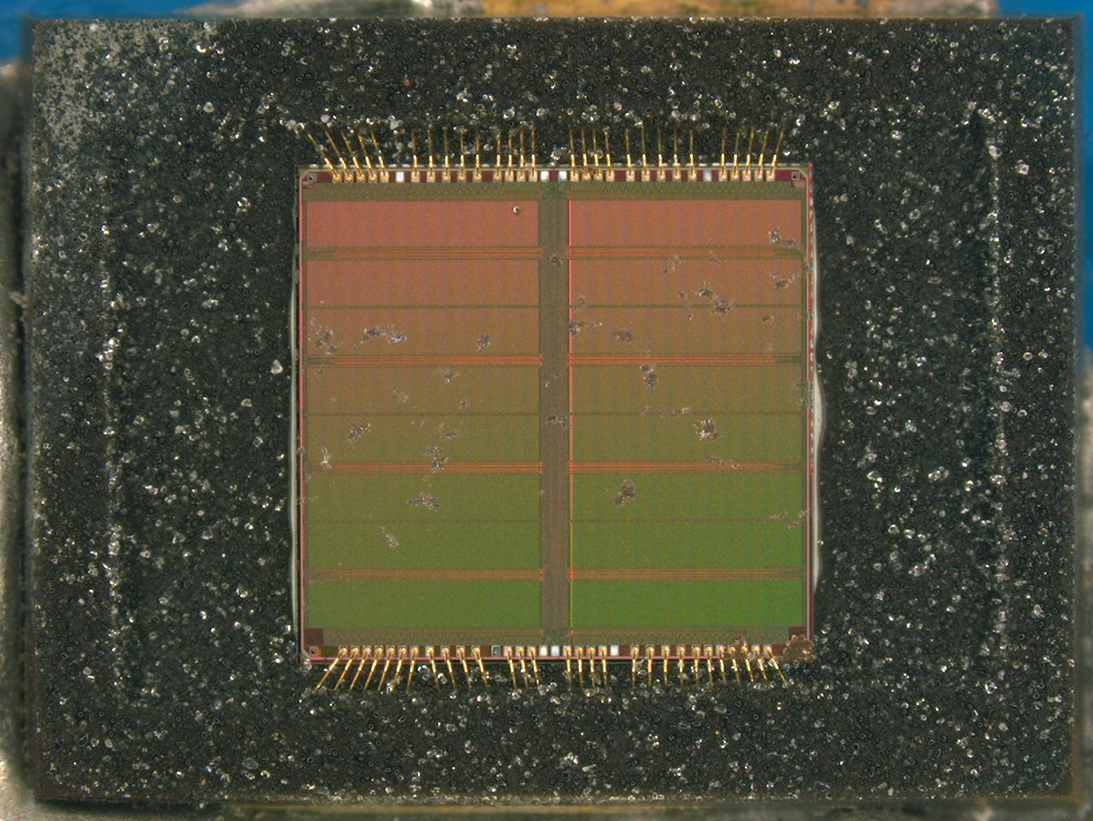
De-Encapsulated View
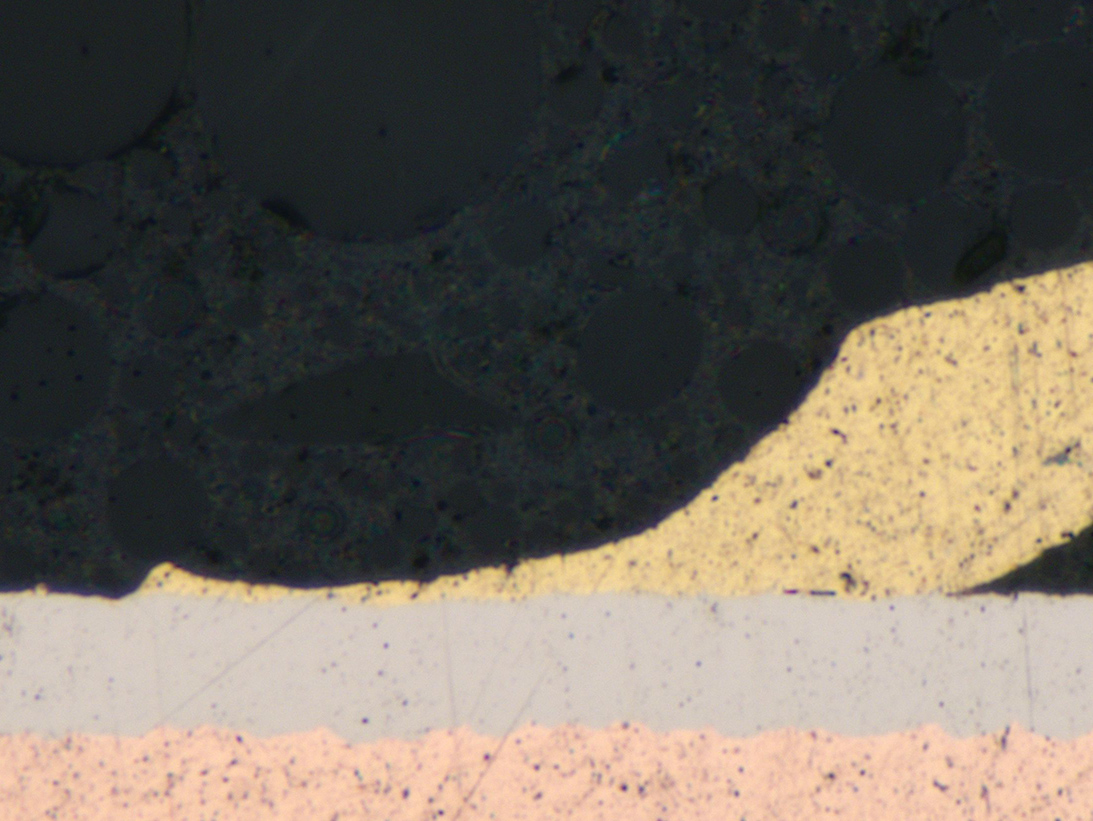
Cross-Section View of Bond
Cross-Section View of Die
De-Encapsulation of BGA
Die Markings
Ball Shear
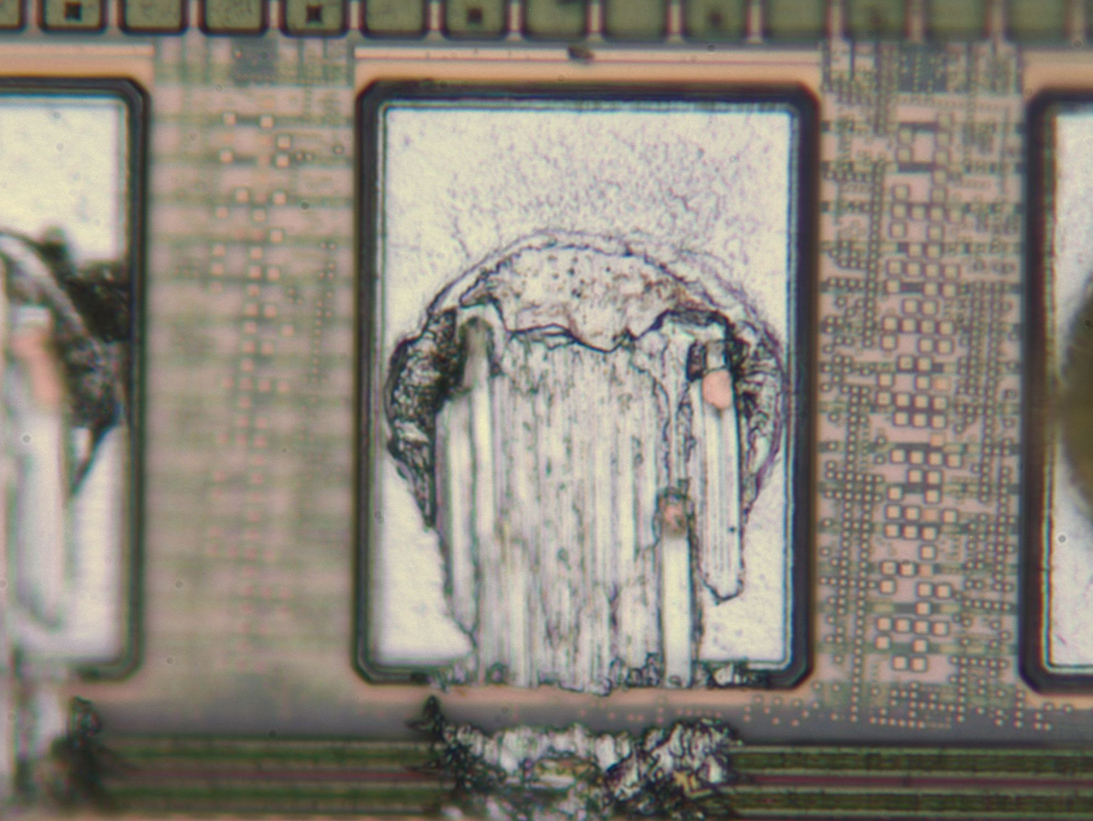
SEM Image of Die Chip Out
SEM Image of Bond Splash
SEM Image of Wedge bond
Cross-Sectional Image
Overall Optical View
Die Metal Inspection
Failure Modes of Microcircuits that can be revealed by DPA:
Failure modes of Microcircuits will vary base on construction and application:
- Loss of Hermeticity/EMC delamination/moisture sensitivity/glass seals
- Wire bonding damage/ bimetallic intermetallic compound
- Die-scribing defects
- Pure tin at external surfaces and internal surface
- Undisclosed product changes
Applicable Industries:
- Space
- Aerospace
- Military Terrestrial
- Automotive/Commercial
- Mainframe Computers
Military Standards:
- MIL-PRF-38535
- MIL-STD-1580/Req 16
- MIL-STD-883 various Methods
Microcircuit Testing Methods
MIL-STD-1580 Requirements
MIL-STD-883 Test Methods
- External Visual – Method 2009
- Physical Dimensions
- Lead Finish Verification
- X-ray Radiography Method 2012
- Particle Induce Noise Detection Method 2020
- Acoustic Microscopy J-STD-035 (PEM) and/or Dye Impregnation Method 1013
- Seal/Hermeticity Method 1014
- Internal Gas Analysis Method 1018
- Internal Visual Inspection Method 2010
- Bond-Strength Testing Method 2011
- Dye-Shear Testing Method 2019
- SEM Metal Inspection Method 2018
- Prohibited Materials Analysis Req. 9